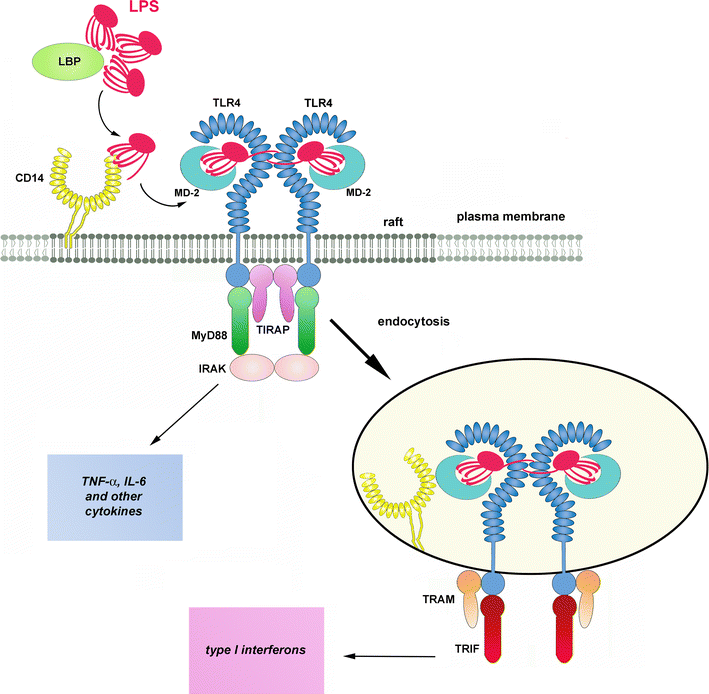
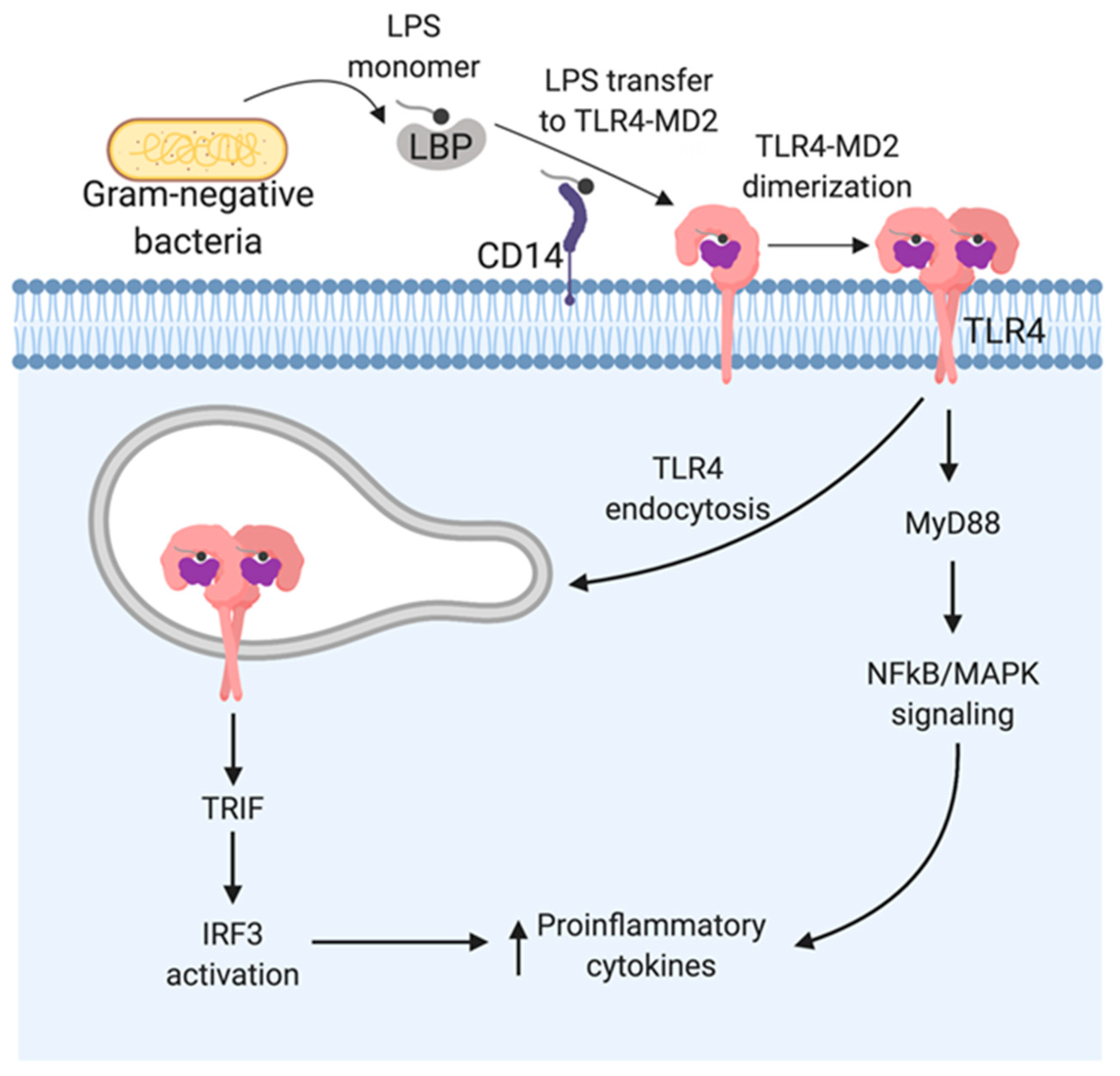
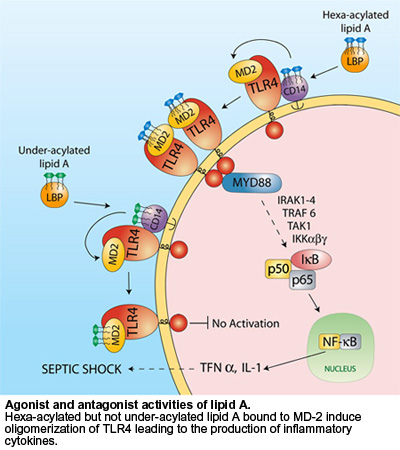
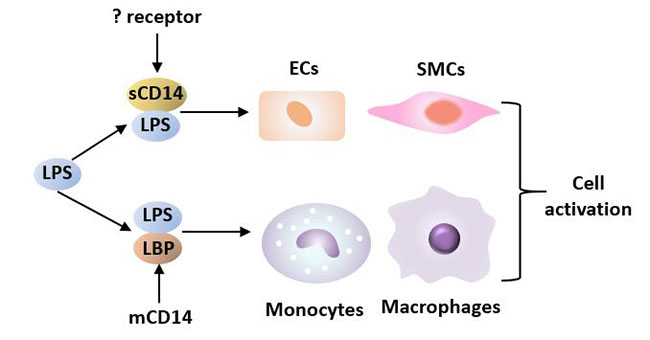
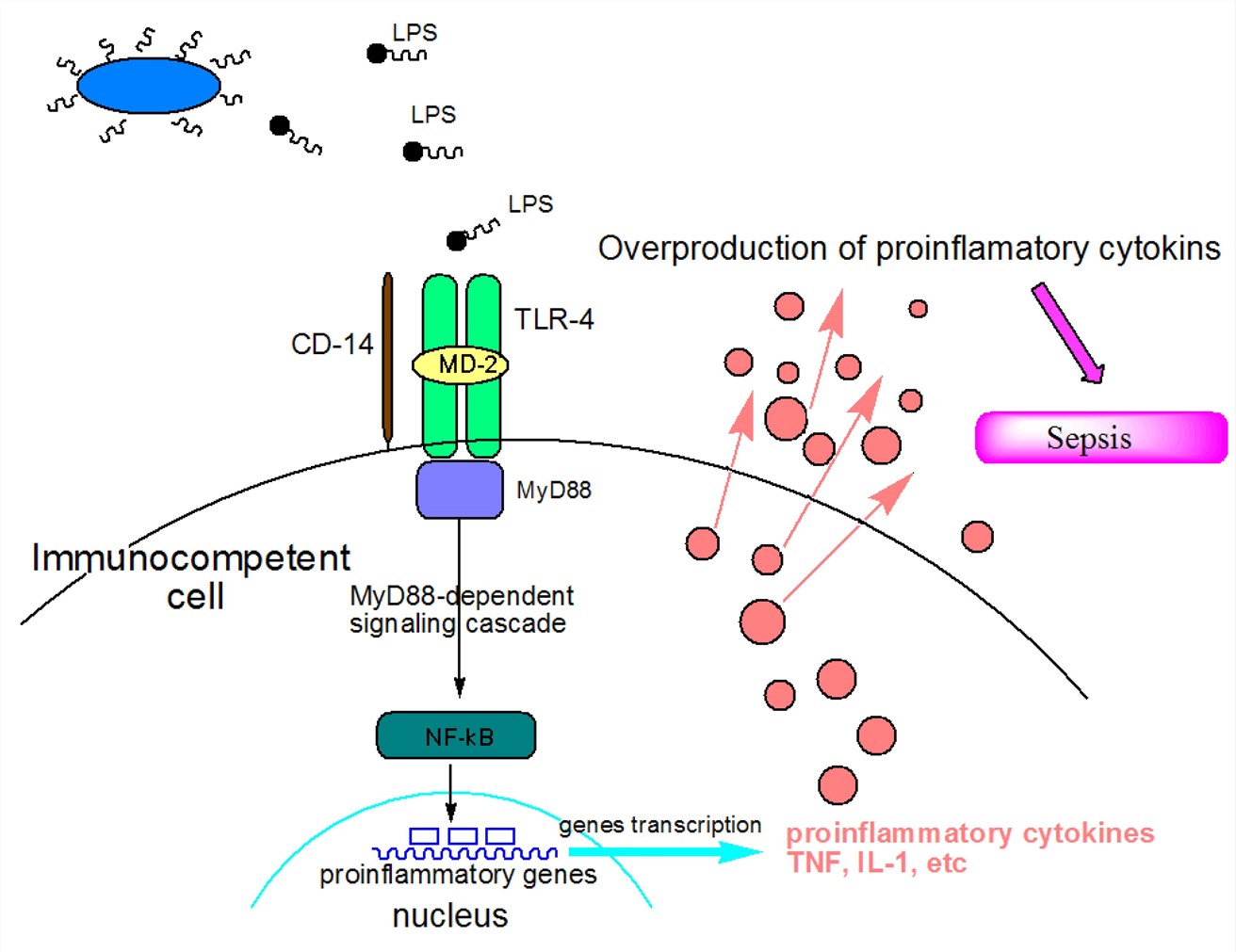
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1–IKKϵ–IRF3 axis activation - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Overview of LPS/TLR-4 signaling pathway. Notes: LPS is delivered to... | Download Scientific Diagram
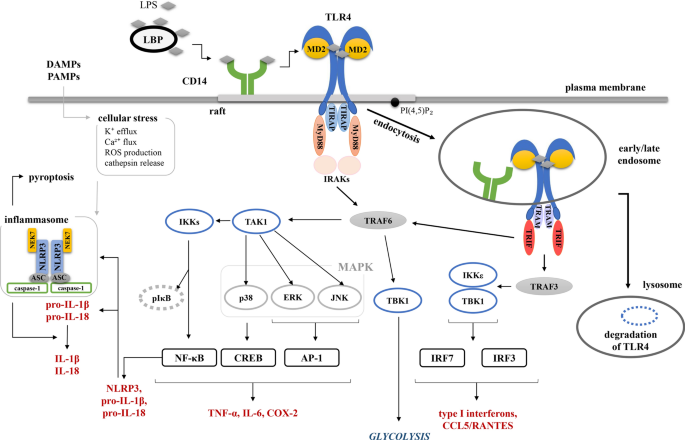
TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling | SpringerLink

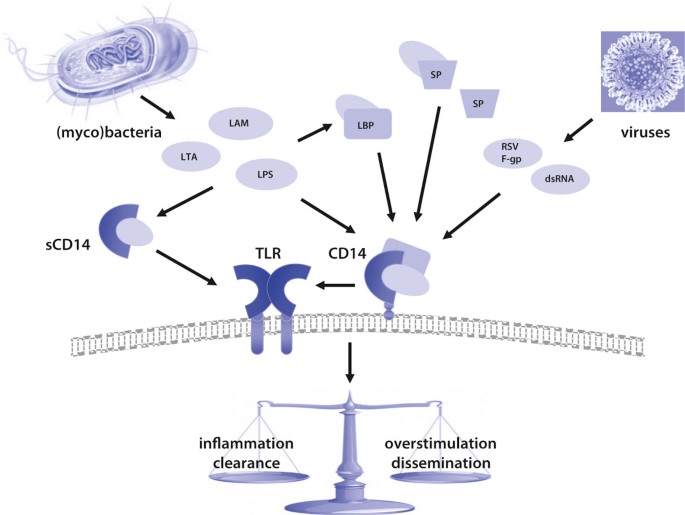
Monoclonal Antibodies to Murine Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Binding Protein (LBP) Protect Mice from Lethal Endotoxemia by Blocking Either the Binding of LPS to LBP or the Presentation of LPS/LBP Complexes to CD14 | The

CD14 dependence of TLR4 endocytosis and TRIF signaling displays ligand specificity and is dissociable in endotoxin tolerance | PNAS

The TLR4 signaling pathway. TLR4 is activated by LPS, whereas CD14 and... | Download Scientific Diagram

Co-operation of TLR4 and raft proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. - Abstract - Europe PMC
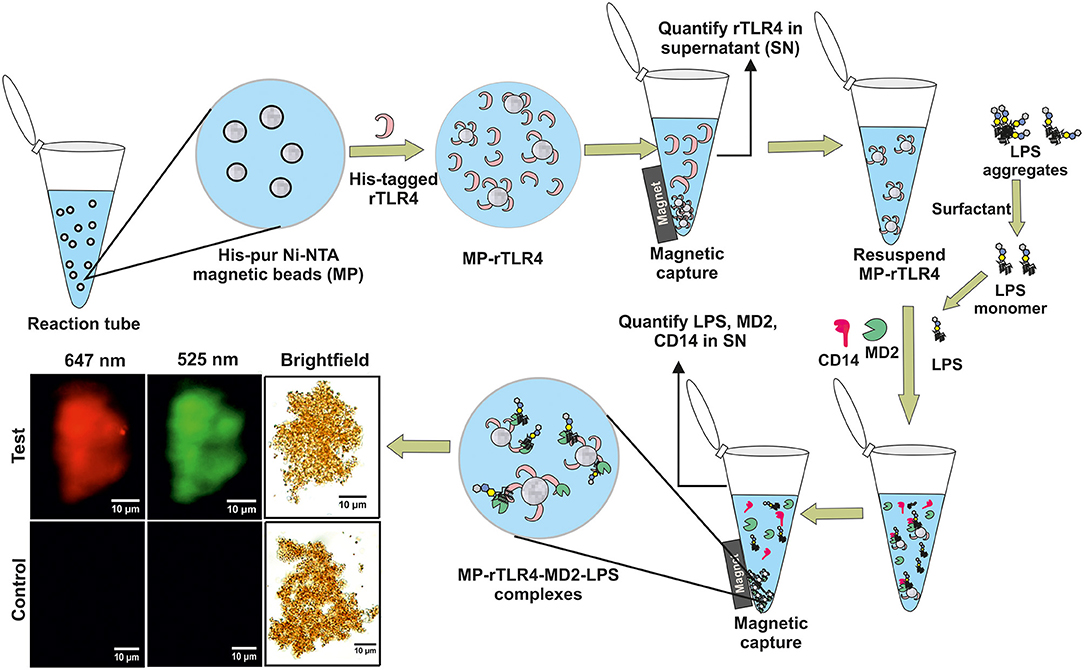
Frontiers | A Single Step in vitro Bioassay Mimicking TLR4-LPS Pathway and the Role of MD2 and CD14 Coreceptors | Immunology

JCI - Plasma CD14 decreases monocyte responses to LPS by transferring cell-bound LPS to plasma lipoproteins

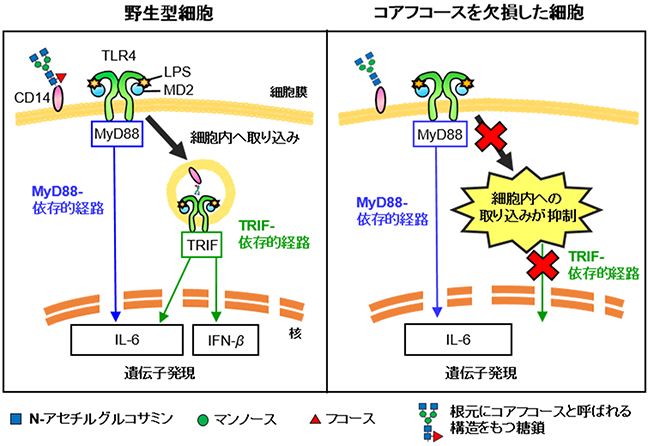
Mechanisms of Toll-like Receptor 4 Endocytosis Reveal a Common Immune-Evasion Strategy Used by Pathogenic and Commensal Bacteria - ScienceDirect

CD14 recycling modulates LPS‐induced inflammatory responses of murine macrophages - Ciesielska - - Traffic - Wiley Online Library

Apolipoprotein CI enhances the biological response to LPS via the CD14/TLR4 pathway by LPS-binding elements in both its N- and C-terminal helix - Journal of Lipid Research